This week the IRS released two new sets of rules impacting Section 125 Cafeteria Plans. Notice 2020-33 provides permanent rule changes that include an increase in the amount of unused benefits that Health FSA plans may allow plan participants to rollover from one plan year to the next. Notice 2020-29 provides temporary rules designed to improve employer sponsored group health benefits for eligible employees in response to the coronavirus pandemic. The relief provided under each notice is optional for employers. Employers who choose to take advantage of any of the offered plan options will be required to notify eligible employees and will eventually be required to execute written plan amendments.
Notice 2020-33 modifies the amount of annual rollover of unused benefits that Health FSA plans may offer to Plan participants. Up until now, rollovers have been limited to $500 per Plan Year. The new rule sets the annual rollover limit to 20% of the statutory maximum annual employee Health FSA contribution for the applicable Plan Year. Because the statutory maximum is indexed for inflation, most years it increases (in mandated increments of $50).
The notice provides that the increased rollover amount may apply to Plan Years beginning on or after January 1, 2020. Because the corresponding annual Health FSA employee contribution limit for those Plan Years is $2,750, the annual rollover limit may be increased up to $550.
The relief provided under Notice 2020-29 falls into two major categories, both of which apply only for calendar year 2020. First, the IRS introduces several significant exceptions to the mid-year change of election rules generally applicable to Section 125 Cafeteria Plans. Second, the notice contains a special grace period which offers Health Flexible Spending Arrangement (FSA) and Dependent Care Assistance Program (DCAP) Participants additional time to incur eligible expenses during 2020.
The temporary exceptions to mid-year participant election change rules for 2020 authorize employers to allow employees who are eligible to participate in a Section 125 Cafeteria Plan to:
None of the above described election changes require compliance with the consistency rules which typically apply for mid-year Section 125 Cafeteria Plan election changes. They also do not require a specific impact from the coronavirus pandemic for the employee.
Employers have the ability to limit election changes that would otherwise be permissible under the exceptions permitted by Notice 2020-29 so long as the limitations comply with the Section 125 non-discrimination rules. For allowable Health FSA or DCAP election changes, employers may limit the amount of any election reduction to the amount previously reimbursed by the plan. Interestingly, even though new elections to make Health FSA and DCAP contributions may not be retroactive, Notice 2020-29 provides that amounts contributed to a Health FSA after a revised mid-year election may be used for any medical expense incurred during the first Plan Year that begins on or after January 1, 2020.
For the election change described in item 3 above, the enrolled employee must make a written attestation that any coverage being dropped is being immediately replaced for the applicable individual. Employers are allowed to rely on the employee’s written attestation without further documentation unless the employer has actual knowledge that the attestation is false.
The special grace period introduced in Notice 2020-29 allows all Health FSAs and DCAPs with a grace period or Plan Year ending during calendar year 2020 to allow otherwise eligible expenses to be incurred by Plan Participants until as late as December 31, 2020. This temporary change will provide relief to non-calendar year based plans. Calendar year Health FSA plans that offer rollovers of unused benefits will not benefit from this change.
The notice does clarify that this special grace period is permitted for non-calendar year Health FSA plans even if the plan provides rollover of unused benefits. Previous guidance had prohibited Health FSA plans from offering both grace periods and rollovers but Notice 2020-29 provides a limited exception to that rule.
The notice raises one issue for employers to consider before amending their plan to offer the special grace period. The special grace period will adversely affect the HSA contribution eligibility of individuals with unused Health FSA benefits at the end of the standard grace period or Plan Year for which a special grace period is offered. This will be of particular importance for employers with employees who may be transitioning into a HDHP group health plan for the first time at open enrollment.
As mentioned above, employers wishing to incorporate any of the allowable changes offered under Notices 2020-29 and 2020-33 will be required to execute written amendments to their Plan Documents and the changes should be reflected in the Plan’s Summary Plan Description and/or a Summary of Material Modification. Notice 2020-29 requires that any such Plan Amendment must be executed by the Plan Sponsor no later than December 31, 2021.
The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (CARES ACT) was signed into law by the President on Friday.
There are three direct inclusions that immediately expand the usage of health savings accounts (HSA), flexible spending accounts (FSA), and health reimbursement arrangements (HRA) for employees.
1. Telehealth services can now be covered pre-deductible under a High Deductible Health Plan. The end date of this provision is Dec 21, 2021.
2. Over the counter (OTC) drugs and medicines are now eligible for reimbursement from an HSA, FSA or HRA. This is a permanent change.
3. Menstrual products are now eligible for reimbursement from an HSA, FSA or HRA. This is a permanent change.
The IRS has recently issued Notice 2019-45, which increases the scope of preventive care that can be covered by a high deductible health plan (“HDHP”) without eliminating the covered person’s ability to maintain a health savings account (“HSA”).
Since 2003, eligible individuals whose sole health coverage is a HDHP have been able to contribute to HSAs. The contribution to the HSA is not taxed when it goes into the HSA or when it is used to pay health benefits. It can for example be used to pay deductibles or copays under the HDHP. But it can also be used as a kind of supplemental retirement plan to pay Medicare premiums or other health expenses in retirement, in which case it is more tax-favored than even a regular retirement plan.
As the name suggests, a HDHP must have a deductible that exceeds certain minimums ($1,350 for self-only HDHP coverage and $2,700 for family HDHP coverage for 2019, subject to cost of living changes in future years). However, certain preventive care (for example, annual physicals and many vaccinations) is covered without having to meet the deductible. In general, “preventive care” has been defined as care designed to identify or prevent illness, injury, or a medical condition, as opposed to care designed to treat an existing illness, injury, or condition.
Notice 2019-45 expands the existing definition of preventive care to cover medical expenses which, although they may treat a particular existing chronic condition, will prevent a future secondary condition. For example, untreated diabetes can cause heart disease, blindness, or a need for amputation, among other complications. Under the new guidance, a HDHP will cover insulin, treating it as a preventative for those other conditions as opposed to a treatment for diabetes.
The Notices states that in general, the intent was to permit the coverage of preventive services if:
The Notice is in general good news for those covered by HDHPs. However, it has two major limitations:
Given the expansion of the types of preventive coverage that a HDHP can cover, and the tax advantages of an HSA to employees, employers who have not previously implemented a HDHP or HSA may want to consider doing so now. However, as with any employee benefit, it is important to consider both the potential demand for the benefit and the administrative cost.
Late May 2019, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) announced the 2020 limits for contributions to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and limits for High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs). These inflation adjustments are provided for under Internal Revenue Code Section 223.
For the 2020 calendar year, an HDHP is a health plan with an annual deductible that is not less than $1,400 for self-only coverage and $2,800 for family coverage. 2020 annual out-of-pocket expenses (deductibles, copayments and other amounts, excluding premiums) cannot exceed $6,900 for self-only coverage and $13,800 for family coverage.
For individuals with self-only coverage under an HDHP, the 2020 annual contribution limit to an HSA is $3,550 and for an individual with family coverage, the HSA contribution limit is $7,100.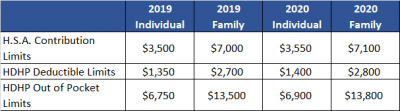
No change was announced to the HSA catch-up contribution limit. If an individual is age 55 or older by the end of the calendar year, he or she can contribute an additional $1,000 to his or her HSA. If married and both spouses are age 55, each individual can contribute an additional $1,000 into his or her individual account.
For married couples that have family coverage where both spouses are over age 55, each spouse can take advantage of the $1,000 catch-up, but in order to get the full $9,100 contribution, they will need to use two accounts. The contribution cannot be maximized with only one account. One individual would contribute the family coverage maximum plus his or her individual catch-up, and the other would contribute the catch-up maximum to his or her individual account.
On May 4, 2017, the IRS released Revenue Procedure 2017-37 setting dollar limitations for health savings accounts (HSAs) and high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) for 2018. HSAs are subject to annual aggregate contribution limits (i.e., employee and dependent contributions plus employer contributions). HSA participants age 55 or older can contribute additional catch-up contributions. Additionally, in order for an individual to contribute to an HSA, he or she must be enrolled in a HDHP meeting minimum deductible and maximum out-of-pocket thresholds. The contribution, deductible and out-of-pocket limitations for 2018 are shown in the table below (2017 limits are included for reference).
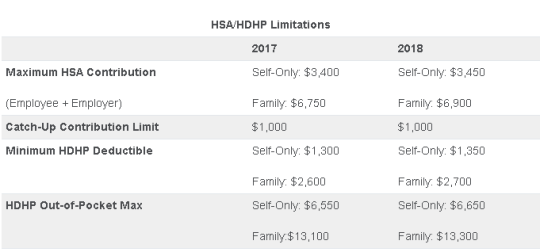
Note that the Affordable Care Act (ACA) also applies an out-of-pocket maximum on expenditures for essential health benefits. However, employers should keep in mind that the HDHP and ACA out-of-pocket maximums differ in a couple of respects. First, ACA out-of-pocket maximums are higher than the maximums for HDHPs. The ACA’s out-of-pocket maximum was identical to the HDHP maximum initially, but the Department of Health and Human Services (which sets the ACA limits) is required to use a different methodology than the IRS (which sets the HSA/HDHP limits) to determine annual inflation increases. That methodology has resulted in a higher out-of-pocket maximum under the ACA. The ACA out-of-pocket limitations for 2018 were announced are are $7350 for single and $14,700 for family.
Second, the ACA requires that the family out-of-pocket maximum include “embedded” self-only maximums on essential health benefits. For example, if an employee is enrolled in family coverage and one member of the family reaches the self-only out-of-pocket maximum on essential health benefits ($7,350 in 2018), that family member cannot incur additional cost-sharing expenses on essential health benefits, even if the family has not collectively reached the family maximum ($14,700 in 2018).
The HDHP rules do not have a similar rule, and therefore, one family member could incur expenses above the HDHP self-only out-of-pocket maximum ($6,650 in 2018). As an example, suppose that one family member incurs expenses of $10,000, $7,350 of which relate to essential health benefits, and no other family member has incurred expenses. That family member has not reached the HDHP maximum ($14,700 in 2018), which applies to all benefits, but has met the self-only embedded ACA maximum ($7,350 in 2018), which applies only to essential health benefits. Therefore, the family member cannot incur additional out-of-pocket expenses related to essential health benefits, but can incur out-of-pocket expenses on non-essential health benefits up to the HDHP family maximum (factoring in expenses incurred by other family members).
Employers should consider these limitations when planning for the 2018 benefit plan year and should review plan communications to ensure that the appropriate limits are reflected.
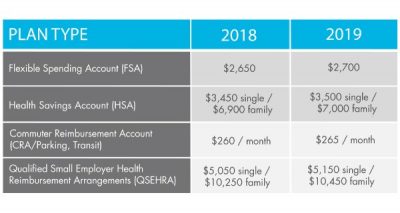
Today the IRS released Revenue Procedure 2016-55 confirming a $50 increase in the health FSA contribution limit to $2,600.
With the passing of the ACA, employee contributions to an FSA were initially limited to $2500 per plan year. This has increased since 2014 to adjust for inflation with the limit being bumped up slightly to $2550 for 2015 & 2016 plan years.
Now, for health FSA plan years beginning on or after January 1, 2017, we have a new increase in the salary reduction contribution limit to $2,600. Be sure to double-check your Section 125 cafeteria plan document to confirm that it automatically incorporates these health FSA cost-of-living increases or to see if you need to specifically request to have the cap increased.
Earlier this year, the IRS also announced the inflation adjusted amounts for 2017 HSA contributions in Revenue Procedure 2016-28. For individuals in self-only coverage, the 2017 contribution limit will increase to $3,400 (up from $3,350). The family coverage contribution limit remains at $6,750 again in 2017.
The Affordable Care Act (“ACA”), introduced in 2014 the Transitional Reinsurance Fee (“Fee”) in an effort to fund reinsurance payments to health insurance issuers that cover high-risk individuals in the individual market and to stabilize insurance premiums in the market for the 2014 through 2016 years. The Fee has also been instituted to pay administrative costs related to the Early Retiree Reinsurance Program.
BACKGROUND ON TRANSITIONAL REINSURANCE PROGRAM
The ACA established a transitional reinsurance program to provide payments to health insurance issuers that cover high risk individuals in an attempt to evenly spread the financial risk of issuers. The program is designed to provide issuers with greater payment stability as insurance market reforms are implemented and the state-based health insurance exchanges/marketplaces facilitate increased enrollment. It is expected that the program will reduce the uncertainty of insurance risk in the individual market by partially offsetting issuers’ risk associated with high-cost enrollees. In an effort to fund the program, the ACA created the Fee which is a temporary fee that is assessed on health insurance issuers and plan sponsors of self-funded health plans. The Fee is applicable for the 2014, 2015 and 2016 years and is deductible as an ordinary and necessary business expense.
The Fee is generally applicable to all health insurance plans providing major medical coverage including sponsors of self-insured group health plans. Major medical coverage is defined as health coverage for a broad range of services and treatments, including diagnostic and preventive services, as well as medical and surgical conditions in inpatient, outpatient and emergency room settings. Since COBRA continuation coverage generally qualifies as major medical coverage, the Fee will also apply in this instance. It does not, however, apply to employer provided major medical coverage that is secondary to Medicare.
The Fee, as currently structured, does not apply to various other types of plans including (but not limited to) health savings accounts (H.S.A.s), employee assistance plans (EAP) or wellness programs that do not provide major medical coverage, health reimbursement arrangements integrated with a group health plan (HRA), health flexible spending accounts (FSA) and coverage that consists of only excepted benefits (e.g. stand-alone dental and vision).
AMOUNT OF THE FEE
The Fee for the 2015 benefit year is equal to $44 per covered life. It is expected that the Fee for the 2015 benefit year will generate approximately $8 billion in revenue. The Fee for the 2016 year is expected to be $27 per covered life and will raise approximately $5 billion in revenue. Thereafter, the Fee is set to expire and no longer be applicable. The fee for 2014 was $63 per covered life.
REPORTING THE NUMBER OF COVERED LIVES AND PAYING THE FEE
The 2015 ACA Transitional Reinsurance Program Annual Enrollment and Contributions Submission Form will be available on www.pay.gov on October 1, 2015. The form for 2014 is also available on this website. Please note there is a separate form for each benefit year. For the 2015 year, the number of covered lives must be reported to the Department no later than November 16, 2015. The Department will then notify reporting organizations no later than December 15, 2015 the amount of the fee that will be due and payable.
As with the 2014 benefit year, the Department of Health and Human Services has given contributing entities two different options to make the payment. Under the first option, the first portion of the Fee ($33 per covered life) is due and payable no later than January 15, 2016 (30 days after issuance of the notice from the Department). This portion of the Fee will cover reinsurance payments and administrative expenses. The second portion of the Fee ($11 per covered life) will cover Treasury’s administrative costs associated with the Early Retiree Reinsurance Program and will be due no later than November 15, 2016.
Under the second payment option, contributing entities can opt to pay the full amount ($44 per covered life) by January 15, 2016.
As the number of covered lives is due to be reported no later than November 16th of this year, employers should review their types of health coverage and determine which plans are subject to the Fee. Employers that have fully insured plans should be on the lookout for potential increased premiums as the insurance carrier is responsible to report and pay the Fee on behalf of the plan in these instances. Those with self funded medical coverage need to be sure to report and pay the fe