Page 2 of 2
Congress and the IRS were busy changing laws governing employee benefit plans and issuing new guidance under the ACA in late 2015. Some of the results of that year-end governmental activity include the following:
The PATH Act, enacted by Congress and signed into law on December 18, 2015, made some the following changes to federal statutory laws governing employee benefit plans:
On December 16, 2015, the IRS issued Notice 2015-87, providing guidance on employee accident and health plans and employer shared-responsibility obligations under the ACA. Guidance provided under Notice 2015-87 applies to plan years that begin after the Notice’s publication date (December 16th), but employers may rely upon the guidance provided by the Notice for periods prior to that date.
Notice 2015-87 covers a wide-range of topics from employer reporting obligations under the ACA to the application of Health Savings Account rules to rules for identifying individuals who are eligible for benefits under plans administered by the Department of Veterans Affairs. Following are some of the highlights from Notice 2015-87, with a focus on provisions that are most likely to impact non-governmental employers.
The Affordable Care Act (“ACA”), introduced in 2014 the Transitional Reinsurance Fee (“Fee”) in an effort to fund reinsurance payments to health insurance issuers that cover high-risk individuals in the individual market and to stabilize insurance premiums in the market for the 2014 through 2016 years. The Fee has also been instituted to pay administrative costs related to the Early Retiree Reinsurance Program.
BACKGROUND ON TRANSITIONAL REINSURANCE PROGRAM
The ACA established a transitional reinsurance program to provide payments to health insurance issuers that cover high risk individuals in an attempt to evenly spread the financial risk of issuers. The program is designed to provide issuers with greater payment stability as insurance market reforms are implemented and the state-based health insurance exchanges/marketplaces facilitate increased enrollment. It is expected that the program will reduce the uncertainty of insurance risk in the individual market by partially offsetting issuers’ risk associated with high-cost enrollees. In an effort to fund the program, the ACA created the Fee which is a temporary fee that is assessed on health insurance issuers and plan sponsors of self-funded health plans. The Fee is applicable for the 2014, 2015 and 2016 years and is deductible as an ordinary and necessary business expense.
The Fee is generally applicable to all health insurance plans providing major medical coverage including sponsors of self-insured group health plans. Major medical coverage is defined as health coverage for a broad range of services and treatments, including diagnostic and preventive services, as well as medical and surgical conditions in inpatient, outpatient and emergency room settings. Since COBRA continuation coverage generally qualifies as major medical coverage, the Fee will also apply in this instance. It does not, however, apply to employer provided major medical coverage that is secondary to Medicare.
The Fee, as currently structured, does not apply to various other types of plans including (but not limited to) health savings accounts (H.S.A.s), employee assistance plans (EAP) or wellness programs that do not provide major medical coverage, health reimbursement arrangements integrated with a group health plan (HRA), health flexible spending accounts (FSA) and coverage that consists of only excepted benefits (e.g. stand-alone dental and vision).
AMOUNT OF THE FEE
The Fee for the 2015 benefit year is equal to $44 per covered life. It is expected that the Fee for the 2015 benefit year will generate approximately $8 billion in revenue. The Fee for the 2016 year is expected to be $27 per covered life and will raise approximately $5 billion in revenue. Thereafter, the Fee is set to expire and no longer be applicable. The fee for 2014 was $63 per covered life.
REPORTING THE NUMBER OF COVERED LIVES AND PAYING THE FEE
The 2015 ACA Transitional Reinsurance Program Annual Enrollment and Contributions Submission Form will be available on www.pay.gov on October 1, 2015. The form for 2014 is also available on this website. Please note there is a separate form for each benefit year. For the 2015 year, the number of covered lives must be reported to the Department no later than November 16, 2015. The Department will then notify reporting organizations no later than December 15, 2015 the amount of the fee that will be due and payable.
As with the 2014 benefit year, the Department of Health and Human Services has given contributing entities two different options to make the payment. Under the first option, the first portion of the Fee ($33 per covered life) is due and payable no later than January 15, 2016 (30 days after issuance of the notice from the Department). This portion of the Fee will cover reinsurance payments and administrative expenses. The second portion of the Fee ($11 per covered life) will cover Treasury’s administrative costs associated with the Early Retiree Reinsurance Program and will be due no later than November 15, 2016.
Under the second payment option, contributing entities can opt to pay the full amount ($44 per covered life) by January 15, 2016.
As the number of covered lives is due to be reported no later than November 16th of this year, employers should review their types of health coverage and determine which plans are subject to the Fee. Employers that have fully insured plans should be on the lookout for potential increased premiums as the insurance carrier is responsible to report and pay the Fee on behalf of the plan in these instances. Those with self funded medical coverage need to be sure to report and pay the fe
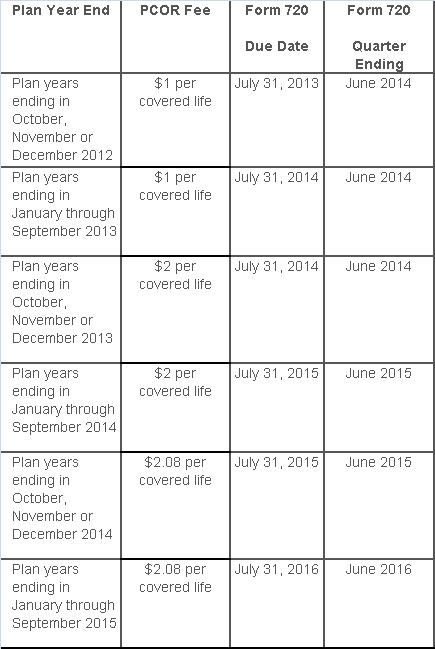
The Affordable Care Act added a patient-centered outcomes research (PCOR) fee on health plans to support clinical effectiveness research. The PCOR fee applies to plan years ending on or after Oct. 1, 2012, and before Oct. 1, 2019. The PCOR fee is due by July 31 of the calendar year following the close of the plan year. For plan years ending in 2014, the fee is due by July 31, 2015.
PCOR fees are required to be reported annually on Form 720, Quarterly Federal Excise Tax Return, for the second quarter of the calendar year. The due date of the return is July 31. Plan sponsors and insurers subject to PCOR fees but not other types of excise taxes should file Form 720 only for the second quarter, and no filings are needed for the other quarters. The PCOR fee can be paid electronically or mailed to the IRS with the Form 720 using a Form 720-V payment voucher for the second quarter. According to the IRS, the fee is tax-deductible as a business expense.
The PCOR fee is assessed based on the number of employees, spouses and dependents that are covered by the plan. The fee is $1 per covered life for plan years ending before Oct. 1, 2013, and $2 per covered life thereafter, subject to adjustment by the government. For plan years ending between Oct. 1, 2014, and Sept. 30, 2015, the fee is $2.08. The Form 720 instructions are expected to be updated soon to reflect this increased fee.
This chart summarizes the fee schedule based on the plan year end and shows the Form 720 due date. It also contains the quarter ending date that should be reported on the first page of the Form 720 (month and year only per IRS instructions). The plan year end date is not reported on the Form 720.
For insured plans, the insurance company is responsible for filing Form 720 and paying the PCOR fee. Therefore, employers with only fully- insured health plans have no filing requirement.
If an employer sponsors a self-insured health plan, the employer must file Form 720 and pay the PCOR fee. For self-insured plans with multiple employers, the named plan sponsor is generally required to file Form 720. A self-insured health plan is any plan providing accident or health coverage if any portion of such coverage is provided other than through an insurance policy.
Since the fee is a tax assessed against the plan sponsor and not the plan, most funded plans subject to ERISA must not pay the fee using plan assets since doing so would be considered a prohibited transaction by the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL). The DOL has provided some limited exceptions to this rule for plans with multiple employers if the plan sponsor exists solely for the purpose of sponsoring and administering the plan and has no source of funding independent of plan assets.
Plans sponsored by all types of employers, including tax-exempt organizations and governmental entities, are subject to the PCOR fee. Most health plans, including major medical plans, prescription drug plans and retiree-only plans, are subject to the PCOR fee, regardless of the number of plan participants. The special rules that apply to Health Reimbursement Accounts (HRAs) and Health Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) are discussed below.
Plans exempt from the fee include:
If a plan sponsor maintains more than one self-insured plan, the plans can be treated as a single plan if they have the same plan year. For example, if an employer has a self-insured medical plan and a separate self-insured prescription drug plan with the same plan year, each employee, spouse and dependent covered under both plans is only counted once for purposes of the PCOR fee.
The IRS has created a helpful chart showing how the PCOR fee applies to common types of health plans.
Health Reimbursement Accounts (HRAs) - Nearly all HRAs are subject to the PCOR fee because they do not meet the conditions for exemption. An HRA will be exempt from the PCOR fee if it provides benefits only for dental or vision expenses, or it meets the following three conditions:
Health Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) - A health FSA is exempt from the PCOR fee if it satisfies an availability condition and a maximum benefit condition.
Additional special rules for HRAs and FSAs . Once an employer determines that its HRA or FSA is subject to the PCOR fee, the employer should consider the following special rules:
The IRS provides different rules for determining the average number of covered lives (i.e., employees, spouses and dependents) under insured plans versus self-insured plans. The same method must be used consistently for the duration of any policy or plan year. However, the insurer or sponsor is not required to use the same method from one year to the next.
A plan sponsor of a self-insured plan may use any of the following three
methods to determine the number of covered lives for a plan year:
1. Actual count method. Count the covered lives on each day of the plan year and divide by the number of days in the plan year.
Example: An employer has 900 covered lives on Jan. 1, 901 on Jan. 2, 890 on
Jan. 3, etc., and the sum of the lives covered under the plan on each day of
the plan year is 328,500. The average number of covered lives is 900 (328,500 ÷
365 days).
2. Snapshot method. Count the covered lives on a single day in each quarter (or more than one day) and divide the total by the number of dates on which a count was made. The date or dates must be consistent for each quarter. For example, if the last day of the first quarter is chosen, then the last day of the second, third and fourth quarters should be used as well.
Example: An employer has 900 covered lives on Jan. 15, 910 on April 15, 890 on
July 15, and 880 on Oct. 15. The average number of covered lives is 895 [(900 +
910+ 890+ 880) ÷ 4 days].
As an alternative to counting actual lives, an employer can count the number of
employees with self-only coverage on the designated dates, plus the number of
employees with other than self-only coverage multiplied by 2.35.
3. Form 5500 method. If a Form 5500 for a plan is filed before the due date of the Form 720 for that year, the plan sponsor can determine the number of covered lives based on the Form 5500. If the plan offers just self-only coverage, the plan sponsor adds the participant counts at the beginning and end of the year (lines 5 and 6d on Form 5500) and divides by 2. If the plan also offers family or dependent coverage, the plan sponsor adds the participant counts at the beginning and end of the year (lines 5 and 6d on Form 5500) without dividing by 2.
Example: An employer offers single and family coverage with a plan year ending
on Dec. 31. The 2013 Form 5500 is filed on June 5, 2014, and reports 132
participants on line 5 and 148 participants on line 6d. The number of covered
lives is 280 (132 + 148).
To evaluate liability for PCOR fees, plan sponsors should identify all of their plans that provide medical benefits and determine if each plan is insured or self-insured. If any plan is self-insured, the plan sponsor should take the following actions:
Even small employers notsubject to the Affordable Care Act’s (ACA) coverage mandate can’t reimburse employees for nongroup health insurance coverage purchased on a public exchange, the Internal Revenue Service confirmed. But small employers providing premium reimbursement in 2014 are being offered transition relief through mid-2015.
IRS Notice 2015-17, issued on Feb. 18, 2015, is another in a series of guidance from the IRS reminding employers that they will run afoul of the ACA if they use health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs) or other employer payment plans—whether with pretax or post-tax dollars—to reimburse employees for individual policy premiums, including policies available on ACA federal or state public exchanges.
This time the warning is aimed at small employers—those with fewer than 50 full-time employees or equivalent workers. While small organizations are not subject to the ACA’s “shared responsibility” employer mandate to provide coverage or pay a penalty (aka Pay or Play), if they do provide health coverage it must meet a range of ACA coverage requirements.
“The agencies have taken the position that employer payment plans are group health plans, and thus must comply with the ACA’s market reforms,” noted Timothy Jost, J.D., a professor at the Washington and Lee University School of Law, in a Feb. 19 post on the Health Affairs Blog. “A group health plan must under these reforms cover at least preventive care and may not have annual dollar limits. A premium payment-only HRA or other payment arrangement that simply pays employee premiums does not comply with these requirements. An employer that offers such an arrangement, therefore, is subject to a fine of $100 per employee per day. (An HRA integrated into a group health plan that, for example, helps with covering cost-sharing is not a problem).”
Transition Relief
The notice provides transition relief for small employers that used premium payment arrangements for 2014. Small employers also will not be subject to penalties for providing payment arrangements for Jan. 1 through June 30, 2015. These employers must end their premium reimbursement plans by that time. This relief does not extend to stand-alone HRAs or other arrangements used to reimburse employees for medical expenses other than insurance premiums.
No similar relief was given for large employers (those with 50 or more full-time employees or equivalents) for the $100 per day per employee penalties. Large employers are required to self-report their violation on the IRS’s excise tax form 8928 with their quarterly filings.
“Notice 2015-17 recognizes that impermissible premium-reimbursement arrangements have been relatively common, particularly in the small-employer market,” states a benefits brief from law firm Spencer Fane. “And although the ACA created “SHOP Marketplaces” as a place for small employers to purchase affordable [group] health insurance, the notice concedes that the SHOPs have been slow to get off the ground. Hence, this transition relief.”
Subchapter S Corps.
The notice states that Subchapter S closely held corporations may pay for or reimburse individual plan premiums for employee-shareholders who own at least 2 percent of the corporation. “In this situation, the payment is included in income, but the 2-percent shareholder can deduct the premiums for tax purposes,” Jost explained. The 2-percent shareholder may also be eligible for premium tax credits through the marketplace SHOP Marketplace if he or she meets other eligibility requirements.
Tricare
Employers can pay for some or all of the expenses of employees covered by Tricare—a Department of Defense program that provides civilian health benefits for military personnel (including some members of the reserves), military retirees and their dependents—if the payment plan is integrated with a group health plan that meets ACA coverage requirements.
Higher Pay Is Still OK
One option that the IRS will allow employers is to simply increase an employee’s taxable wages in lieu of offering health insurance. “As long as the money is not specifically designated for premiums, this would not be a premium payment plan,” said Jost. “The employer could even give the employee general information about the marketplace and the availability of premium tax credits as long as it does not direct the employee to a specific plan.”
But if the employer pays or reimburses premiums specifically, “even if the payments are made on an after-tax basis, the arrangement is a noncompliant group health plan and the employer that offers it is subject to the $100 per day per employee penalty,” Jost warned.
“Small employers now have just over four months in which to wind down any impermissible premium-reimbursement arrangement,” the Spencer Fane brief notes. “In its place, they may wish to adopt a plan through a SHOP Marketplace. Although individuals may enroll through a Marketplace during only annual or special enrollment periods, there is no such limitation on an employer’s ability to adopt a plan through a SHOP.”
On December 22, 2014, the Departments of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued proposed regulations for changes to the Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC).
The proposed regulations clarify when and how a plan administrator or insurer must provide an SBC, shortens the SBC template, adds a third cost example, and revises the uniform glossary. The proposed regulations provide new information and also incorporate several FAQs that have been issued since the final SBC regulations were issued in 2012.
These proposed changes are effective for plan years and open enrollment period beginning on or after September 1, 2015. Comments on the proposed regulations will be accepted until March 2,2015 and are encourages on many of the provisions.
New Template
The new SBC template eliminates a significant amount of information that the Departments characterized as not being required by law and/or as having been identified by consumer testing as less useful for choosing coverage.
The sample completed SBC template for a standard group health plan has been reduced from four double-sided pages to two-and-a-half double-sided pages. Some of the other changes include:
Glossary Revisions
Revisions to the uniform glossary have also been proposed. The glossary must be available to plan participants upon request. Some definitions have been changed and new medical terms such as claim, screening, referral and specialty drug have been added. Additional terms related to health care reform such as individual responsibility requirement, minimum value and cost-sharing reductions have also been added.
Paper vs Electronic Distribution
SBCs may continue to be provided electronically to group plan participants in connection with their online enrollment or online renewal of coverage. SBCs may also be provided electronically to participants who request an SBC online. These individuals must also have the option to receive a paper copy upon request.
SBCs for self-insured non-federal government plans may continue to be provided electronically if the plan conforms to either the electronic distribution requirements that apply ERISA plan or the rules that apply to individual health insurance coverage.
Types of Plans to Which SBCs Apply
The regulations confirm that SBCs are not required for expatriate health plans, Medicare Advantage plans or plans that qualify as excepted benefits. Excepted benefits include:
SBCs are required for:
The Department of Labor has just published a series of FAQs regarding premium reimbursement arrangements. Specifically, the FAQs address the following arrangements:
Situation #1: An arrangement in which an employer offers an employee cash to reimburse the purchase of an individual market policy.
When an employer provides cash reimbursement to the employee to purchase an individual medical policy, the DOL takes the position that the employer’s payment arrangement is part of a plan, fund, or other arrangement established or maintained for the purpose of providing medical care to employees, regardless of whether the employer treats the money as pre or post tax to the employee. Therefore, the arrangement is considered a group health plan that is subject to the market reform provisions of the Affordable Care Act applicable to group health plans and because it does not comply (and cannot comply) with such provisions, it may be subject to penalties.
Situation #2: An arrangement in which an employer offers employees with high cost claims a choice between enrollment in its group health plan or cash.
The DOL takes the position that offering a choice between enrolling in the group health plan or cash only to employees with a high claims risk would be discriminatory based on one or more health factors. The DOL states that such arrangements will violate such nondiscrimination provisions regardless of whether (1) the cash payment is treated by the employer as pre-tax or post-tax to the employee, (2) the employer is involved in the selection or purchase of any individual medical policy, or (3) the employee obtains any individual health insurance. The DOL also notes that such an arrangement, depending on facts and circumstances, could result in discrimination under an employer’s cafeteria plan.
Situation #3: An arrangement where an employer cancels its group policy, sets up a reimbursement plan (like an HRA) that works with health insurance brokers or agents to help employees select individual insurance policies, and allows eligible employees to access the premium tax credits for Marketplace coverage.
The DOL takes the position that such an arrangement is a considered a group health plan and, therefore, employees participating in such arrangement are ineligible for premium tax credits (or cost-sharing reductions) for Marketplace coverage. The DOL also takes the position that such arrangements are subject to the market reform provisions of the ACA and cannot be integrated with individual market policies to satisfy the market reforms. Thus, such arrangements can trigger penalties.
Key Takeaway
There has been quite a bit of banter regarding whether any of the foregoing arrangements could be an effective way for employers to avoid complying with the market reforms and other provisions of the Affordable Care Act applicable to group health plans. These FAQs are a strong indication that the DOL will be forceful in its interpretation and enforcement of these provisions.
Many employers originally thought they could shift health costs to the government by sending their employees to a health insurance Exchange/Marketplace with a tax-free contribution of cash to help pay premiums, but the Obama administration has squashed this idea in a new ruling. Such arrangements do not satisfy requirements under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), the Obama administration said, and employers could now be subject to a tax penalty of $100 a day — or $36,500 a year — for each employee who goes into the individual Marketplace/Exchange for health coverage.
The ruling this month, by the Internal Revenue Service, prevents any “dumping” of employees into the exchanges by employers.
Under a main provision in the health care law, employers with 50 or more employees are required to offer health coverage to full-time workers, or else the employer may be subject to penalties.
Many employers had concluded that it would be cheaper to provide each employee with a lump sum of money to buy insurance on an exchange, instead of providing employer-sponsored health coverage directly to employees as they had in the past.
But the Obama administration has now raised objections in an authoritative Q&A document recently released by the IRS, in consultation with other agencies.
The health law, known as the Affordable Care Act (ACA), was intended to build on the current system of employer-based health insurance. The administration wants employers to continue to provide coverage to workers and their families and do not see the introduction of ACA as an eventual erosion of employer provided coverage.
Employer contributions to sponsored health coverage, which averages more than $5,000 a year per employee, are not counted as taxable income to workers. But the IRS has said employers could not meet their obligations under ACA by simply reimbursing employees for some or all of their premium costs from the marketplace/exchange.
Christopher E. Condeluci, a former tax and benefits counsel to the Senate Finance Committee, said the recent IRS ruling was significant because it made clear that “an employee cannot use tax-free contributions from an employer to purchase an insurance policy sold in the individual health insurance market, inside or outside an exchange.”
If an employer wants to help employees buy insurance on their own, Condeluci said, they can give the employee higher pay, in the form of taxable wages. But in such cases, he said, the employer and the employee would owe payroll taxes on those wages, and the change could be viewed by workers as reducing a valuable benefit.
A tax partner from a large accounting firm has also said the ruling could disrupt reimbursement arrangements used in many industries.
For decades, many employers have been assisting employees by reimbursing them for health insurance premiums and out-of-pocket costs associated with their health coverage. The new federal ruling eliminates many of those arrangements, commonly known as Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) or employer payment plans, by imposing an unusually punitive penalty. The IRS has said that these employer payment plans are considered to be group health plans, but they do not satisfy requirements of the Affordable Care Act for health coverage.
Under the law, insurers may not impose annual limits on the dollar amount of benefits for any individual, and they must provide certain preventive services, like mammograms and colon cancer screenings, without co-payments or other charges.
But the administration has said that employer payment plans or HRAs do not meet these requirements.
This ruling was released as the Obama administration rushed to provide guidance to employers and insurers who are beginning to review coverage options for 2015.
The Department of Health and Human Services said it would provide financial assistance to certain insurers that experience unexpected financial losses this year. Administration officials hope the payments will stabilize medical premiums and prevent rate increases that are associated with the required policy changes as a result of ACA.
Republicans want to block these payments, however, as they see them as a bailout for insurance companies who originally supported the president’s health care law.
Stay tuned for more updates on ACA as they are released. Should you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact our office.
If your company offered either a Health Reimbursement Account (HRA) or Medical Expense Reimbursement Plan (MERP) as part of your employee benefits package in 2012, you must report and pay the PCORI fee for your 2012 plan year no later than July 31, 2013. Please note that the penalty for not filing can be as high as $10,000 per month.
You must use the IRS Form 720 to report and pay the PCORI fee.
If you used a third party administrator to handle the administration of your HRA or MERP plan, they should have provided you with the necessary information to complete Form 720 as they are not permitted to file this with the IRS on your behalf.
Please let us know if you have any questions.