PCORI Filing Due to IRS by Aug. 1
Transparency in Coverage mandates and COVID-19 considerations continue to dominate the discussion in the employee benefits compliance space this summer, but an “old faithful” reporting requirement looms soon: the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) filing and fee. The Affordable Care Act imposes this annual per-enrollee fee on insurers and sponsors of self-funded medical plans to fund research into the comparative effectiveness of various medical treatment options.
The typical due date for the PCORI fee is July 31, but because that date falls on a Sunday in 2022, the effective due date is pushed to the next business day, which is Aug. 1.
The filing and payment due by Aug. 1, 2022, is required for policy and plan years that ended during the 2021 calendar year. For plan years that ended Jan. 1, 2021 – Sept. 30, 2021, the fee is $2.66 per covered life. For plan years that ended Oct. 1, 2021 – Dec. 31, 2021 (including calendar year plans that ended Dec. 31, 2021), the fee is calculated at $2.79 per covered life.
Insurers report on and pay the fee for fully insured group medical plans. For self-funded plans, the employer or plan sponsor submits the fee and accompanying paperwork to the IRS. Third-party reporting and payment of the fee (for example, by the self-insured plan sponsor’s third-party claim payor) is not permitted.
An employer that sponsors a self-insured health reimbursement arrangement (HRA) along with a fully insured medical plan must pay PCORI fees based on the number of employees (dependents are not included in this count) participating in the HRA, while the insurer pays the PCORI fee on the individuals (including dependents) covered under the insured plan. Where an employer maintains an HRA along with a self-funded medical plan and both have the same plan year, the employer pays a single PCORI fee based on the number of covered lives in the self-funded medical plan and the HRA is disregarded.
PCORI fee reporting and payment
The IRS collects the fee from the insurer or, in the case of self-funded plans, the plan sponsor in the same way many other excise taxes are collected. Although the PCORI fee is paid annually, it is reported (and paid) with the Form 720 filing for the second calendar quarter (the quarter ending June 30). Again, the filing and payment is typically due by July 31 of the year following the last day of the plan year to which the payment relates, but this year the due date pushes to Aug. 1.
Calculating the PCORI fee
IRS regulations provide three options for determining the average number of covered lives: actual count, snapshot and Form 5500 method.
Actual count: The average daily number of covered lives during the plan year. The plan sponsor takes the sum of covered lives on each day of the plan year and divides the number by the days in the plan year.
Snapshot: The sum of the number of covered lives on a single day (or multiple days, at the plan sponsor’s election) within each quarter of the plan year, divided by the number of snapshot days for the year. Here, the sponsor may calculate the actual number of covered lives, or it may take the sum of (i) individuals with self-only coverage, and (ii) the number of enrollees with coverage other than self-only (employee-plus one, employee-plus family, etc.), and multiply by 2.35. Further, final rules allow the dates used in the second, third and fourth calendar quarters to fall within three days of the date used for the first quarter (in order to account for weekends and holidays). The 30th and 31st days of the month are both treated as the last day of the month when determining the corresponding snapshot day in a month that has fewer than 31 days.
Form 5500: If the plan offers family coverage, the sponsor simply reports and pays the fee on the sum of the participants as of the first and last days of the year (recall that dependents are not reflected in the participant count on the Form 5500). There is no averaging. In short, the sponsor is multiplying its participant count by two, to roughly account for covered dependents.
The U.S. Department of Labor says the PCORI fee cannot be paid from ERISA plan assets, except in the case of union-affiliated multiemployer plans. In other words, the PCORI fee must be paid by the plan sponsor; it cannot be paid in whole or part by participant contributions or from a trust holding ERISA plan assets. The PCORI expense should not be included in the plan’s cost when computing the plan’s COBRA premium. The IRS has indicated the fee is, however, a tax-deductible business expense for sponsors of self-funded plans.
Although the DOL’s position relates to ERISA plans, please note the PCORI fee applies to non-ERISA plans as well and to plans to which the ACA’s market reform rules don’t apply, like retiree-only plans.
How to file IRS Form 720
The filing and remittance process to the IRS is straightforward and unchanged from last year. On Page 2 of Form 720, under Part II, the employer designates the average number of covered lives under its “applicable self-insured plan.” As described above, the number of covered lives is multiplied by the applicable per-covered-life rate (depending on when in 2021 the plan year ended) to determine the total fee owed to the IRS.
The Payment Voucher (720-V) should indicate the tax period for the fee is “2nd Quarter.”
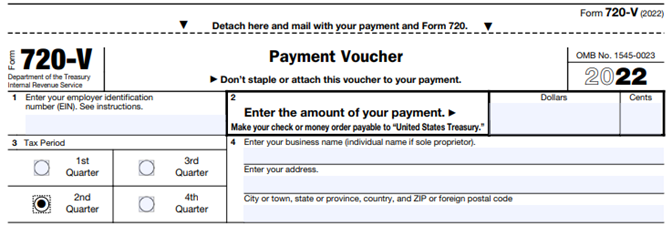
Failure to properly designate “2nd Quarter” on the voucher will result in the IRS’ software generating a tardy filing notice, with all the incumbent aggravation on the employer to correct the matter with IRS.
You missed a past PCORI payment. Now what?
An employer that overlooks reporting and payment of the PCORI fee by its due date should immediately, upon realizing the oversight, file Form 720 and pay the fee (or file a corrected Form 720 to report and pay the fee, if the employer timely filed the form for other reasons but neglected to report and pay the PCORI fee). Remember to use the Form 720 for the appropriate tax year to ensure that the appropriate fee per covered life is noted.
The IRS might levy interest and penalties for a late filing and payment, but it has the authority to waive penalties for good cause. The IRS’s penalties for failure to file or pay are described here.
The IRS has specifically audited employers for PCORI fee payment and filing obligations. Be sure, if you are filing with respect to a self-funded program, to retain documentation establishing how you determined the amount payable and how you calculated the participant count for the applicable plan year.


