The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) announced on February 20,2015 a special enrollment period (SEP) for individuals and families who did not have health coverage in 2014 and are subject to the fee or “shared responsibility payment” when they file their 2014 taxes in states which use the Federally-facilitated Marketplaces (FFM). This special enrollment period will allow those individuals and families who were unaware or didn’t understand the implications of this new requirement to enroll in 2015 health insurance coverage through the FFM.
For those who were unaware or didn’t understand the implications of the fee for not enrolling in coverage, CMS will provide consumers with an opportunity to purchase health insurance coverage from March 15 to April 30. If consumers do not purchase coverage for 2015 during this special enrollment period, they may have to pay a fee when they file their 2015 income taxes.
Those eligible for this special enrollment period live in states with a Federally-facilitated Marketplace and:
The special enrollment period announced today will begin on March 15, 2015 and end at 11:59 pm E.S.T. on April 30, 2015. If a consumer enrolls in coverage before the 15th of the month, coverage will be effective on the first day of the following month.
This year’s tax season is the first time individuals and families will be asked to provide basic information regarding their health coverage on their tax returns. Individuals who could not afford coverage or met other conditions may be eligible to receive an exemption for 2014. To help consumers who did not have insurance last year determine if they qualify for an exemption, CMS also launched a health coverage tax exemption tool today on HealthCare.gov and CuidadodeSalud.gov.
“We recognize that this is the first tax filing season where consumers may have to pay a fee or claim an exemption for not having health insurance coverage,” said CMS Administrator Marilyn Tavenner. “Our priority is to make sure consumers understand the new requirement to enroll in health coverage and to provide those who were not aware or did not understand the requirement with an opportunity to enroll in affordable coverage this year.”
Most taxpayers will only need to check a box when they file their taxes to indicate that they had health coverage in 2014 through their employer, Medicare, Medicaid, veterans care or other qualified health coverage that qualifies as “minimum essential coverage.” The remaining taxpayers will take different steps. It is expected that 10 to 20 percent of taxpayers who were uninsured for all or part of 2014 will qualify for an exemption from the requirement to have coverage. A much smaller fraction of taxpayers, an estimated 2 to 4 percent, will pay a fee because they made a choice to not obtain coverage and are not eligible for an exemption.
Americans who do not qualify for an exemption and went without health coverage in 2014 will have to pay a fee – $95 per adult or 1 percent of their income, whichever is greater – when they file their taxes this year. The fee increases to $325 per adult or 2% of income for 2015. Individuals taking advantage of this special enrollment period will still owe a fee for the months they were uninsured and did not receive an exemption in 2014 and 2015. This special enrollment period is designed to allow such individuals the opportunity to get covered for the remainder of the year and avoid additional fees for 2015.
The Administration is committed to providing the information and tools tax filers need to understand the new requirements. Part of this outreach effort involves coordinating efforts with nonprofit organizations and tax preparers who provide resources to consumers and offer on the ground support. If consumers have questions about their taxes, need to download forms, or want to learn more about the fee for not having insurance, they can find information and resources at www.HealthCare.gov/Taxes or www.IRS.gov. Consumers can also call the Marketplace Call Center at 1-800-318-2596. Consumers who need assistance filing their taxes can visit IRS.gov/VITA or IRS.gov/freefile.
Consumers seeking to take advantage of the special enrollment period can find out if they are eligible by visitinghttps://www.healthcare.gov/get-coverage. Consumers can find local help at: Localhelp.healthcare.gov or call the Federally-facilitated Marketplace Call Center at 1-800-318-2596. TTY users should call 1-855-889-4325. Assistance is available in 150 languages. The call is free.
For more information about Health Insurance Marketplaces, visit: www.healthcare.gov/marketplace
Last week, the IRS issued its “final” versions of the forms 1094-B,1094-C, 1095-B and 1095-C along with instructions for the “B” forms and instructions for the “C” forms. The good news is that the forms are pretty much the same from the drafts released in mid 2014. What has changed is that the revised instructions have filled in some gaps about reporting, some of which are highlighted below:
1. Employers with 50-99 FTEs who were exempt from compliance in 2015 must still file these forms for the 2015 tax year.
2. For employers that cover non-employees (COBRA beneficiaries or retirees being most common), they can use forms 1094-B and 1095-B instead of filing out 1095-C Part III to report for those individuals.
3. With respect to reporting for employees who work for more than one employer member of a controlled group aggregated “ALE”, the employee may receive a report from each separate employer. However, the employer for whom he or she works the most hours in a given month should report for that month.
4. Under the final instructions, a full-time employee of a self-insured employer that accepts a qualifying offer and enrolls in coverage, the employer must provide that employee a 1095-C. The previous draft indicated that it would be enough to simply provide an employee a statement about the offer rather than an actual form
5. For plans that exclude spouses covered or offered health coverage through their own employers, the definition of “offer of health coverage” now provides that an offer to a spouse subject to a reasonable, objective condition is treated as an offer of coverage for reporting purposes.
6. There are some changes with respect to what days can be used to measure the “count” for reporting purposes. Employers are allowed to use the first day of the first payroll period of each month or the last day of the first payroll period of each month, as long as the last day is in the same month as when the payroll period starts. Also, an employer can report offering coverage for a month only if the employer offers coverage for every day of that month. Mid-month eligibilities would presumably be counted as being covered on the first day of the next month. However, in the case of terminations of employment mid-month, the coverage can be treated as offered for the entire month if, but for the termination, the coverage would have continued for the full month.
Now as a refresher about what needs to be filed:
Bear in mind that there is a considerable amount of time between now and the final filing obligation so there may be additional revisions to these instructions, or at least some further clarification. But in the meantime, read the instructions and familiarize yourself with the reporting obligations as well as beginning the steps to collecting the necessary data to make completing the forms next year easier.
Healthcare Reform continues to roll on despite all of its opponents. While 2014 brought the implementation of the health insurance exchanges, the Individual Mandate, and a host of new rules relating to employer-provided health coverage, 2015 marks the start of yet another major component of the Affordable Care Act (ACA): the Employer Mandate.
In the a recent article written by Fisher & Phillips LLP attorney Steven Witt, he discusses the potential risks employers can face if they are not careful in how they implement (and document) their compliance strategies with regards to the Employer Mandate.
The Employer Mandate requires large employers to offer compliant group health coverage to their “full-time employees” and their dependents or face excise tax penalties. Say you are a large employer who has never offered health insurance (or perhaps only to a small subset of your employees). You do not want to bankrupt the company and offer health insurance to your entire workforce, nor do you want to face tax penalties. Instead, you opt for what the Employer Mandate calls for: you offer health insurance coverage to only your full-time employees.
If you decide to only offer coverage to your “full-time” employees, simply setting measurement period dates with your human resources department and running payroll reports to determine who is “full-time” will not sufficiently limit the risk of controversy and potential legal liability. You will be much better off to clearly define these eligibility rules in writing and make sure any old, conflicting eligibility rules are updated.
Leaving existing plan documents and other materials (e.g., employee handbooks) to define health insurance eligibility with something vague like “full-time employees: employees who regularly work 30 or more hours per week,” is only inviting trouble. You will no doubt have employees (with attorneys) who could make plausible arguments that they “regularly” work 30 or more hours a week and can point to your existing written documents as evidence they should have been offered health insurance. Without clearly setting out new eligibility rules, it will be a much steeper uphill battle for the employer to defend itself.
On the other hand, if such employees attempt to claim that they were unfairly denied health insurance coverage, an employer should be on much stronger footing to defend its position that those employees are not “full-time” if it can point to written documentation outlining items such as (a) date ranges used for measurement periods and stability periods; (b) waiting periods for newly-eligible employees; and © how to treat employees in special circumstances, such as those who are promoted from a part-time position to a full-time position, those on a leave of absence, or rehired employees.
If you have not already done this, it is not too late. Even employers subject to the Employer Mandate in 2015 can still timely revise their SPDs or perhaps draft stand-alone benefits eligibility documents or other “wrap” documents to fully outline new eligibility rules. Steven advises employers to pay close attention as additional regulations and agency guidance continues to roll out to ensure they stay in compliance with ERISA, the ACA, and other related federal and state health insurance-related laws.
Form 1095-A is a tax form that will be sent to consumers who have been enrolled in health insurance through the Marketplace in the past year. Just like employees receive a W-2 from their employer, consumer who had a plans on the Marketplace will also receive form 1095-A from the Marketplace, which they will need for taxes. Similar to how households receive multiple W-2s if individuals have multiple jobs, some households will get multiple Form 1095-As if they were covered under different plans or changed plans during the year. The 1095-A forms will be mailed direct to consumer’s last known home address provided to the Marketplace and will be postmarked by February 2, 2015.
Form 1095-A provides information to consumers that is needed to complete Form 8962, Premium Tax Credit (PTC). The Marketplace has also reporting this information to the IRS. Consumers will file Form 8962 with their tax returns if they want to claim the premium tax credit or if they received premium assistance through advance credit payments made to their insurance provider.
Beginning January 1, 2015, employers have new reporting obligations for health plan coverage, to allow the government to administer the “pay or play” penalties to be assessed against employers that do not offer compliant coverage to their full-time employees.
Even though the penalties only apply if there are 100 or more employees for 2015, employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent employees are required to report for 2015. Also, note this reporting is required even if the employer does not maintain any health plan.
Employers that provide self-funded group health coverage also have reporting obligations, to allow the government to administer the “individual mandate” which results in a tax on individuals who do not maintain health coverage.
These reporting obligations will be difficult for most employers to implement. Penalties for non-compliance are high, so employers need to begin now with developing a plan on how they will track and file the required information.
Pay or Play Reporting. Applicable large employers (ALEs) must report health coverage offered to employees for each month of 2015 in an annual information return due early in 2016. ALEs are employers with 50 or more full-time equivalent (FTE) employees. Employees who average 30 hours are counted as one, and those who average less than 30 hours are combined into an equivalent number of 30 hour employees to determine if there are 50 or more FTE employees. All employees of controlled group, or 80% commonly owned employers, are also combined to determine if the 50 FTE threshold is met.
Individual Mandate Reporting. Self-funded employers, including both ALEs and small employers that are not ALEs, must report each individual covered for each month of the calendar year. For fully-insured coverage, the insurance carrier must report individual month by month coverage. The individual mandate reporting is due early in 2016 for each month of 2015.
Which Form? ALE employers have one set of forms to report both the pay or play and the individual mandate information – Forms 1094C and 1095C. Insurers and self-insured employers that are not ALEs use Forms 1094B and 1095B to report the individual mandate information. Information about employee and individual coverage provided on these forms must also be reported by the employer to its employees as well as to COBRA and retiree participants. Forms 1095B and 1095C can be used to provide this information, or employers can provide the information in a different format.
The following chart summaries which returns are filed by employers:
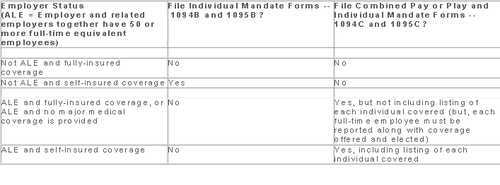
Who Reports? While ALE status is determined on a controlled group basis, each ALE must file separate reports. Employers will need to provide insurance carriers, and third party administrators who process claims for self-funded coverage (if they will assist the employer with reporting), accurate data on the employer for whom each covered employee works. If an employee works for more than one ALE in a controlled group, the employer for whom the highest number of hours is worked does the reporting for that employee.
Due Date for Filing. The due date of the forms matches the due dates of Forms W-2, and employers may provide the required employee statements along with the W-2. Employee reporting is due January 31st and reporting to the IRS is due each February 28th, although the date is extended until March 31st if the forms are filed electronically. If the employer files 250 or more returns, the returns must be filed electronically. Reporting to employees can only be made electronically if the employee has specifically consented to receiving these reports electronically.
Penalties. Failure to file penalties can total $200 per individual for whom information must be reported, subject to a maximum of $3 million per year. Penalties will not be assessed for employers who make a good faith effort to file correct returns for 2015.
What Information is Required? For the pay or play reporting, each ALE must file a Form 1094C reporting the number of its full-time employees (averaging 30 hours) and total employees for each calendar month, whether the ALE is in a “aggregated” (controlled) group, a listing of the name and EIN of the top 30 other entities in the controlled group (ranked by number of full-time employees), and any special transition rules being used for pay or play penalties. ALE’s must also file a 1095C for each employee who was a full-time employee during any calendar month of the year. The 1095C includes the employee’s name, address and SSN, and month by month reporting of whether coverage was offered to the employee, spouse and dependents, the lowest premium for employee only coverage, and identification of the safe-harbor used to determine affordability. This information is used to determine pay or play penalty taxes and to verify the individuals’ eligibility for subsidies toward coverage costs on the Federal and state exchanges.
If the ALE provides self-funded coverage, the ALE must also report on the 1095C the name and SSN of each individual provided coverage for each calendar month. If an employer is not an ALE, but is self-funded, the name and SSN of each covered individual is reported on the 1095B and the 1094B is used to transmit the forms 1095B to the IRS.
A chart is available that sets out what data must be reported on each form, to help employers determine what information they need to track. Click here to access the chart.
Next Steps. Employers will need to determine how much help their insurance carrier or TPA can provide with the reporting, and then the employer’s HR, payroll and IT functions will need to work together to be sure the necessary information is being tracked and can be produced for reporting in January 2016.
Members of the U.S. House of Representatives voted on January 8, 2015 to redefine full-time employment under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) to employees who work at least 40 hours a week rather than 30 hours a week.
The Save American Workers Act, passed the House with a vote of 252-172 with full Republican support and 12 Democratic voters. The legislation would amend the Internal Revenue Code by changing the definition of full-time employee to cover individuals who work, on average, at least 40 hours per week for purposes of the employer mandate to provide minimum essential health care coverage under the ACA.
Despite the bill’s passage in the House, the fate of the bill in the U.S. Senate remains uncertain. In addition, Republicans have not garnered enough support to override the veto promised by President Obama if the bill did pass Congress.
According to Politico, “The House has cleared more than 50 assorted measures to repeal or roll back Obamacare, but this is the first time the House can propel legislation to a GOP-controlled Senate, potentially forcing President Barack Obama to either accept changes to his signature domestic achievement or use his veto power.”
Some supporters of the change, including the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, argue that the current standard deviates from the widely accepted definition of full-time work. It is argued that it provides an incentive for employers to reduce hours, particularly for low-wage workers, to avoid offering healthcare coverage.
This month, employers with 100 or more employees will be required to offer health insurance to at least 70% of employees who works at least 30 hours a week or else pay a penalty.
The NY Times comments:
By adjusting that threshold to 40 hours, Republicans — strongly backed by a number of business groups — said that they would re-establish the traditional 40-hour workweek and prevent businesses cutting costs from radically trimming worker hours to avoid mandatory insurance coverage. They contend that the most vulnerable workers are low-skilled and underpaid, working 30 to 35 hours a week, and now facing cuts to 29 hours or less so their employers do not have to insure them. With passage of the law, those workers would not have to get employer-sponsored health care, and their workweek would remain intact.
Analysis by the Congressional Budget Office found that the bill would increase the U.S. deficit by $53 billion over the course of a decade because fewer employers would pay penalties and one million employees would not have coverage through their job. Democrats cite these reasons as evidence that the bill is simply an attempt to dismantle the ACA.
A central issue of this bill is how far employers would go to avoid mandated coverage. A majority of employees already work 40 hours a week rather than 30. That being said, few employers would cut worker hours from 40 to 29, but many would be willing to cut hours from 40 to 39, the New York Times ventures, “That means raising the definition of a full-time worker under the health care law would put far more workers at risk.”
On December 22, 2014, the Departments of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued proposed regulations for changes to the Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC).
The proposed regulations clarify when and how a plan administrator or insurer must provide an SBC, shortens the SBC template, adds a third cost example, and revises the uniform glossary. The proposed regulations provide new information and also incorporate several FAQs that have been issued since the final SBC regulations were issued in 2012.
These proposed changes are effective for plan years and open enrollment period beginning on or after September 1, 2015. Comments on the proposed regulations will be accepted until March 2,2015 and are encourages on many of the provisions.
New Template
The new SBC template eliminates a significant amount of information that the Departments characterized as not being required by law and/or as having been identified by consumer testing as less useful for choosing coverage.
The sample completed SBC template for a standard group health plan has been reduced from four double-sided pages to two-and-a-half double-sided pages. Some of the other changes include:
Glossary Revisions
Revisions to the uniform glossary have also been proposed. The glossary must be available to plan participants upon request. Some definitions have been changed and new medical terms such as claim, screening, referral and specialty drug have been added. Additional terms related to health care reform such as individual responsibility requirement, minimum value and cost-sharing reductions have also been added.
Paper vs Electronic Distribution
SBCs may continue to be provided electronically to group plan participants in connection with their online enrollment or online renewal of coverage. SBCs may also be provided electronically to participants who request an SBC online. These individuals must also have the option to receive a paper copy upon request.
SBCs for self-insured non-federal government plans may continue to be provided electronically if the plan conforms to either the electronic distribution requirements that apply ERISA plan or the rules that apply to individual health insurance coverage.
Types of Plans to Which SBCs Apply
The regulations confirm that SBCs are not required for expatriate health plans, Medicare Advantage plans or plans that qualify as excepted benefits. Excepted benefits include:
SBCs are required for:
The Affordable Care Act will require Applicable Large Employers (i.e. large employers subject to the employer mandate) and employers sponsoring self-insured plans to comply with new annual IRS reporting requirements. The first reporting deadline will be February 28, 2016 as to the data employers collect during the 2015 calendar year. The reporting provides the IRS with information it needs to enforce the Individual Mandate (i.e. individuals are penalized for not having health coverage) and the Employer Mandate (i.e. large employers are penalized for not offering health coverage to full-time employees). The IRS will also require employers who offer self-insured plans to report on covered individuals.
Large employers and coverage providers must also provide a written statement to each employee or responsible individual (i.e. one who enrolls one or more individuals) identifying the reported information. The written statement can be a copy of the Form.
The IRS recently released draft Forms 1094-C and 1095-C and draft Forms 1094-B and 1095-B, along with draft instructions for each form.
Which Forms Do I File?
When?
Statements to employees and responsible individuals are due annually by January 31. The first statements are due January 31, 2016.
Forms 1094-B, 1095-B, 1094-C and 1095-C are due annually by February 28 (or by March 31, if filing electronically). The first filing is due by February 28, 2016 (or March 31, 2016, if filing electronically).
Even though the forms are not due until 2016, the annual reporting will be based on data from the prior year. Employers need to plan ahead now to collect data for 2015. Many employers have adopted the Look Back Measurement Method Safe Harbor (“Safe Harbor”) to identify full-time employees under the ACA. The Safe Harbor allows employers to “look back” on the hours of service of its employees during 2014 or another measurement period. There are specific legal restrictions regarding the timing and length of the periods under the Safe Harbor, so employers cannot just pick random dates. Employers also must follow various rules to calculate hours of service under the Safe Harbor. The hours of service during the measurement period (which is likely to include most of 2014) will determine whether a particular employee is full-time under the ACA during the 2015 stability period. The stability period is the time during which the status of the employee, as full-time or non-full-time, is locked in. In 2016, employers must report their employees’ full-time status during the calendar year of 2015. Therefore, even though the IRS forms are not due until 2016, an employee’s hours of service in 2014 will determine how an employer reports that employee during each month of 2015. Employers who have not adopted the Safe Harbor should consider doing so because it allows an employer to average hours of service over a 12-month period to determine the full-time status of an employee. If an employer does not adopt the Safe Harbor, the IRS will require the employer to make a monthly determination, which is likely to increase an employer’s potential exposure to penalties.
What Must the Employer Report?
Form 1095-C
There are three parts to Form 1095-C. An applicable large employer must file one Form 1095-C for each full-time employee. If the applicable large employer sponsors self-insured health plans, it must also file Form 1095-C for any employee who enrolls in coverage regardless of the full-time status of that employee.
Form 1095-C requires the employer to identify the type of health coverage offered to a full-time employee for each calendar month, including whether that coverage offered minimum value and was affordable for that employee. Employers must use a code to identify the type of health coverage offered and applicable transition relief.
Employers that offer self-insured health plans also must report information about each individual enrolled in the self-insured health plan, including any full-time employee, non-full-time employee, employee family members, and others.
Form 1094-C
Applicable large employers use Form 1094-C as a transmittal to report employer summary information and transmit its Forms 1095-C to the IRS. Form 1094-C requires employers to enter the name and contact information of the employer and the total number of Forms 1095-C it submits. It also requires information about whether the employer offered minimum essential coverage under an eligible employer-sponsored plan to at least 95% of its full-time employees and their dependents for the entire calendar year, the number of full-time employees for each month, and the total number of employees (full-time or non-full-time) for each month.
Form 1095-B
Employers offering self-insured coverage use Form 1095-B to report information to the IRS about individuals who are covered by minimum essential coverage and therefore are not liable for the individual shared responsibility payment. These employers must file a Form 1095-B for eachindividual who was covered for any part of the calendar year. The employer must make reasonable efforts to collect social security numbers for covered individuals.
Form 1094-B
Employers who file Form 1095-B will use Form 1094-B as a transmittal form. It asks for the name of the employer, the employer’s EIN, and the name, telephone number, and address of the employer’s contact person.
Failure to Report – What Happens?
The IRS will impose penalties for failure to timely provide correct written statements to employees. The IRS will also impose penalties for failure to timely file a correct return. For the 2016 reporting on 2015 data, the IRS will not impose a penalty for good faith compliance. However, the IRS specified that good faith compliance requires that employers provide the statements and file the returns.
On November 7th, 2014, the U.S. Supreme Court agreed to hear King v. Burwell. The case will argue whether or not subsidies in the marketplace should be limited to states with state-run Exchanges. According to the New York Times, “If the challengers are right, millions of people receiving subsidies (through the federal Exchange) would become ineligible for them, destabilizing and perhaps dooming the law.” Arguments are due to begin in December, and a ruling will be issue by next June.
The key question in the case deals with the conflicting IRS ruling stating that “subsidies are allowed whether the exchange is run by a state or by the federal government.” Those challenging the law in this case say that this rule conflicts with the statutory language set forth in the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
Two lower courts, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia in Halbig v. Burwell and the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit in King v. Burwell, have already issued conflicting opinions regarding the IRS’ authority to administer subsidies in federally facilitated Exchanges. In addition, two other cases are being litigated in the lower courts on the same issue. In Pruitt v. Burwell, a district court in Oklahoma ruled against the IRS in September, and a decision in a fourth court case, Indiana v. IRS, is expected shortly. Of course, the Supreme Court ruling could render the lower court decisions moot.
The Department of Labor has just published a series of FAQs regarding premium reimbursement arrangements. Specifically, the FAQs address the following arrangements:
Situation #1: An arrangement in which an employer offers an employee cash to reimburse the purchase of an individual market policy.
When an employer provides cash reimbursement to the employee to purchase an individual medical policy, the DOL takes the position that the employer’s payment arrangement is part of a plan, fund, or other arrangement established or maintained for the purpose of providing medical care to employees, regardless of whether the employer treats the money as pre or post tax to the employee. Therefore, the arrangement is considered a group health plan that is subject to the market reform provisions of the Affordable Care Act applicable to group health plans and because it does not comply (and cannot comply) with such provisions, it may be subject to penalties.
Situation #2: An arrangement in which an employer offers employees with high cost claims a choice between enrollment in its group health plan or cash.
The DOL takes the position that offering a choice between enrolling in the group health plan or cash only to employees with a high claims risk would be discriminatory based on one or more health factors. The DOL states that such arrangements will violate such nondiscrimination provisions regardless of whether (1) the cash payment is treated by the employer as pre-tax or post-tax to the employee, (2) the employer is involved in the selection or purchase of any individual medical policy, or (3) the employee obtains any individual health insurance. The DOL also notes that such an arrangement, depending on facts and circumstances, could result in discrimination under an employer’s cafeteria plan.
Situation #3: An arrangement where an employer cancels its group policy, sets up a reimbursement plan (like an HRA) that works with health insurance brokers or agents to help employees select individual insurance policies, and allows eligible employees to access the premium tax credits for Marketplace coverage.
The DOL takes the position that such an arrangement is a considered a group health plan and, therefore, employees participating in such arrangement are ineligible for premium tax credits (or cost-sharing reductions) for Marketplace coverage. The DOL also takes the position that such arrangements are subject to the market reform provisions of the ACA and cannot be integrated with individual market policies to satisfy the market reforms. Thus, such arrangements can trigger penalties.
Key Takeaway
There has been quite a bit of banter regarding whether any of the foregoing arrangements could be an effective way for employers to avoid complying with the market reforms and other provisions of the Affordable Care Act applicable to group health plans. These FAQs are a strong indication that the DOL will be forceful in its interpretation and enforcement of these provisions.